Demand forecasting is essential to any supply chain management and logistics optimization strategy, helping businesses anticipate customer needs and plan accordingly.
In this guide, you’ll learn what demand forecasting entails, why it matters, and various types and techniques to employ to improve your supply chain.
What Is Demand Forecasting in the Supply Chain?
Demand forecasting in supply chain management refers to the process of demand planning , or predicting the demand of materials to ensure you can deliver the right products and in the right quantities to satisfy customer demand without creating a surplus. Forecast error can result in creating a surplus, which is both wasteful and costly.
Why Is Forecasting Demand Important in the Supply Chain?
Accurate demand forecasting informs strategic and operational planning. You can also think of it as the underlying hypothesis for business activities or the starting point for most supply chain processes, like raw material planning, purchasing, inbound logistics, cash flow, and manufacturing.
For example, demand forecasting for DTC brands impacts various directions, such as how to meet customer demand or allocate resources.
Aligning Supply with Demand
At its core, demand forecasting in ecommerce helps you align supply with customer demand, ensuring that businesses stock the right products at the right time. This alignment is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction, avoiding stockouts and overstocking, and curbing excess inventory and dead stock that tie up capital and storage space.
Additionally, effective demand forecasting for DTC brands supports lean inventory management and faster fulfillment. In other words, teams can make data-driven decisions about product, inventory, and delivery that directly tie back to the customer experience or long-term growth.
Strategic Planning and Resource Allocation
Accurate forecasting enables ecommerce businesses to plan for various activities. For example, a team might launch an email or paid ads campaign ahead of a seasonal surge according to forecasted demand.
Similarly, demand forecasting for ecommerce fulfillment helps brands allocate inventory and staff efficiently (if they handle fulfillment in-house), like increasing warehouse staff or stock ahead of Black Friday.
On the financial end, reliable forecasts support budgeting. For instance, a company may increase production for best-selling items or delay a product launch according to anticipated demand. Forecasts also help teams invest wisely in product development and market expansion, ensuring that resources are channeled correctly.
How Does Demand Forecasting Work?
Demand forecasting relies on two main approaches: qualitative and quantitative forecasting. Both depend on distinct resources or data sets to gather useful, actionable information.
Quantitative forecasting, for instance, uses existing historical data and pre-established demand. It’s ideal when you have sufficient knowledge to lean on, such as financial reports, sales, revenue figures, and website analytics, and can employ techniques like time-series analysis to examine demand.
Qualitative forecasting, on the other hand, uses expert judgment, market research, or customer surveys to estimate demand. It is especially helpful when launching new products or entering unfamiliar markets where historical data is limited.
Most businesses use a hybrid of both, combining data-driven insights with human experience to improve forecasting accuracy.
The 6 Types of Demand Forecasting
In addition to general processes, demand forecasting can be broken down into six different types that inform the scope, timeframe, or data source of the forecast.
Each offers unique insights and is suited to different business needs and market conditions. Some rely on historical, quantitative data; others use qualitative inputs like market trends or expert insight.
1. Passive Demand Forecasting
Passive demand forecasting is ideal for businesses with stable, predictable markets. It relies on historical data and trends to project future demand, assuming that past patterns will continue. This method is less suited for rapidly changing or highly competitive markets where innovation and disruption are common.
2. Active Demand Forecasting
Active demand forecasting takes a more dynamic approach, incorporating current market trends, changes in consumer behavior, and upcoming industry shifts. It’s tailored for businesses in fast-paced environments where supply chain agility and responsiveness are crucial for staying ahead of the curve.
3. Short-term Demand Forecasting
Focusing on the immediate future (typically up to one year ahead), short-term demand forecasting helps businesses manage day-to-day operations and seasonal fluctuations effectively. It’s crucial for inventory management and meeting short-term financial goals.
4. Long-term Demand Forecasting
Looking several years into the future, long-term demand forecasting is used for strategic planning, such as capacity expansion, entering new markets, or launching new products. While inherently more uncertain, it’s vital for guiding long-term business growth and investment decisions.
5. External Demand Forecasting
This approach looks beyond the company’s internal data, considering macroeconomic indicators (such as tariffs), industry trends, and competitive landscape. External demand forecasting is essential for understanding broader market forces and potential supply chain bottlenecks, positioning the business for sustainable growth.
6. Internal Demand Forecasting
Focusing on a company’s own sales and performance data, internal demand forecasting provides insights based on historical sales trends, production capacities, and internal resources. It’s useful for optimizing operational efficiency and resource allocation.
Demand Forecasting Techniques
In addition to types, you can also select the tools or methods you employ. These methods may be qualitative or quantitative and dictate how you forecast demand.
Here are a few examples:
- Collective opinion: A qualitative method that leverages the intuition and experience of the sales team to estimate future demand. It is especially useful when launching new products or entering new markets.
- Customer survey: Surveys provide qualitative information on customer expectations, desires, and needs. This data is useful for creating a sales forecast, but it is harder to predict actual demand.
- Barometric method: A quantitative technique involving economic indicators to predict trends and measure current, past, and future activity.
- Expert opinion: This method involves soliciting expert advice from external contractors to determine future activity. It is a standard example of qualitative demand forecasting.
- Market experiment: Market experiments may be quantitative or qualitative, depending on what you employ. Generally, however, it calls for experiments under controlled conditions to inform retailers on consumer behavior.
- Statistical method: A quantitative demand forecasting example that allows you to identify and analyze the relationships between different variables, establish performance history over time, and identify trends.
Factors Influencing the Customer Demand Life Cycle
Accurate forecasting starts with understanding the factors that shape the customer demand life cycle. While these vary by market and product, recognizing and analyzing them can greatly improve demand forecasting for ecommerce fulfillment.
Seasonality
Seasonal trends have a profound impact on customer demand, with certain products seeing a surge in sales during specific times of the year. Ecommerce businesses must account for seasonality in their demand forecasting to ensure they can meet the increased demand during peak seasons without overstocking in the off-season.
Competition
The competitive landscape can dramatically influence customer demand. New entrants, innovative products, or aggressive pricing strategies by competitors can shift interest away from your products. Keeping a close eye on the competition and adapting your forecasting models accordingly is essential for staying ahead.
Types of Goods
The nature of the products you sell also affects demand forecasting. Perishable goods, high-tech items, and fashion products each have different demand cycles and require different forecasting approaches. Understanding the product life cycle and customer buying patterns is key to accuracy here.
Geography
Geographic factors also play a role. Regional preferences, shipping logistics, and local market conditions all influence demand for certain products. Demand forecasting for DTC brands, in this context, calls for geographic data to optimize inventory distribution and marketing strategies.
How To Forecast Demand
Accurate demand forecasting is valuable to all businesses, but is particularly useful to ecommerce brands where an analysis can support product inventory management and improve the customer experience.
But knowing how to approach something as complex as demand forecasting for ecommerce fulfillment is no small task. Fortunately, some tried and true strategies can make the process easier.
Collect the Right Data
For your demand forecast to be successful, you must ensure that you have the right kind of data. Hone in on the numbers that matter, such as pricing trends and how many people visited your sales channels in a given timeframe.
Try not to focus your data collection efforts on a complete product line. It’s better to concentrate on the products and categories that earn you the most income and are the most popular with customers.
Adjust for Variables
Many factors affect sales data. For your demand forecast to be successful, you need to account for any variables that may sway your data one way or another, such as tariffs or unexpected store closures. You should also account for product-specific variables—seasonality, trends, or lifecycle stage—since these can lead to unpredictable demand spikes or dips.
Document Sales and Demand Trends
Establish a repeatable process for tracking and evaluating your forecasts. A strong system should:
- Show whether forecast accuracy is improving
- Highlight which products need refinement
- Align with your procurement lead time
- Provide insights by customer, branch, brand, product, and category
Budget, Purchase, and Allocate Accordingly
Once your demand forecast is in place, the next step is to turn insights into action. Use your forecast data to guide how, where, and when you purchase inventory, allocate budgets, and position stock.
For example, this may mean increasing purchase orders for high-demand SKUs, delaying replenishment on slow-moving items, or shifting inventory to regional warehouses closer to customer hubs.
Accurate forecasting also allows finance and operations teams to align on working capital needs, marketing spend, and staffing requirements, ensuring that resources are deployed efficiently and at the right time.
By planning around demand rather than reacting to it, ecommerce brands can reduce excess inventory and avoid last-minute supply chain costs.
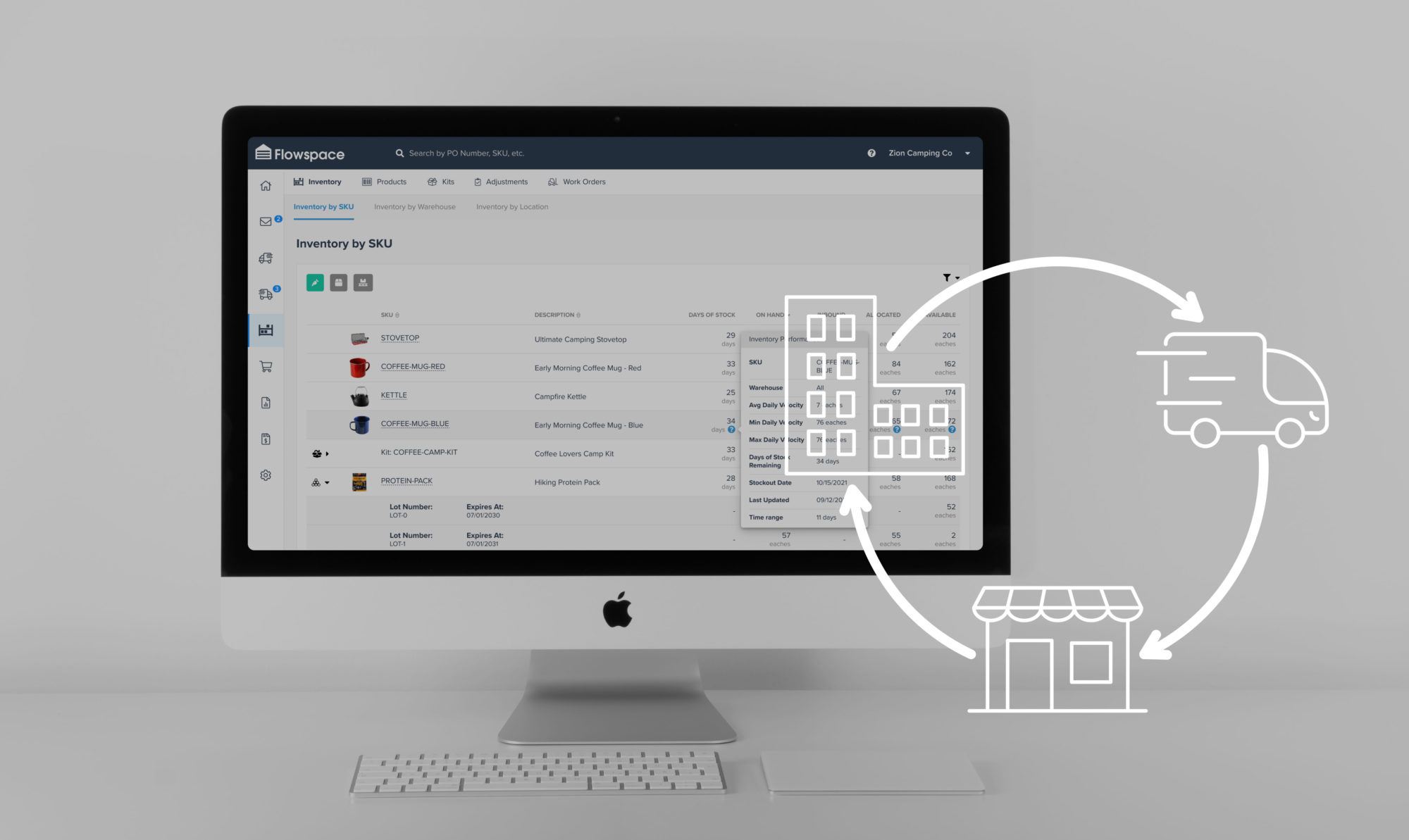
How to Support Demand Forecasting with 3PLs
Partnering with a third-party logistics provider (3PL) can support your forecasting efforts. Choosing advanced options—namely, a fulfillment partner like Flowspace—offers critical real-time visibility, in addition to data insights and distributed warehouse networks.
For instance, real-time visibility from your provider helps you adapt quickly to shifting market conditions and supply chain disruptions. With a clear view into your fulfillment operations, you can reduce costs, optimize your network, and better align inventory with rising or falling demand.
This transparency also supports lean inventory management and operational efficiency. Both of which are critical advantages during volatile conditions like the 2025 global tariffs.
To stay agile and competitive, businesses choose solutions like Flowspace to meet demand and scale faster.
Flowspace Makes Demand Forecasting Easy
Modern ecommerce fulfillment relies on predictive accuracy. With the right tools to support your team, demand forecasting for ecommerce fulfillment helps ensure that products are stored in optimal locations, transit times are minimized, and customer expectations are met.
You can leverage Flowspace’s fulfillment software to inform these time-sensitive business decisions and boost your overall supply chain and inventory management strategy.








